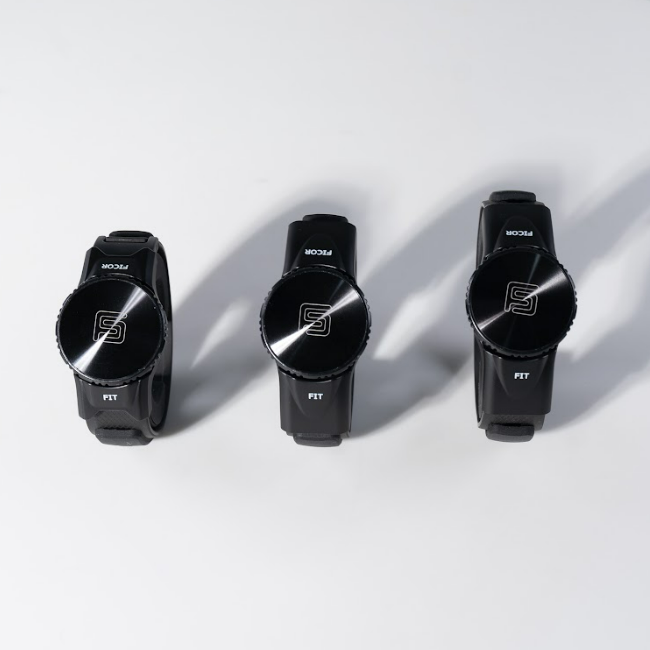
Ships within 10 days.
30 Day Money-Back Guarantee
U.S. Company
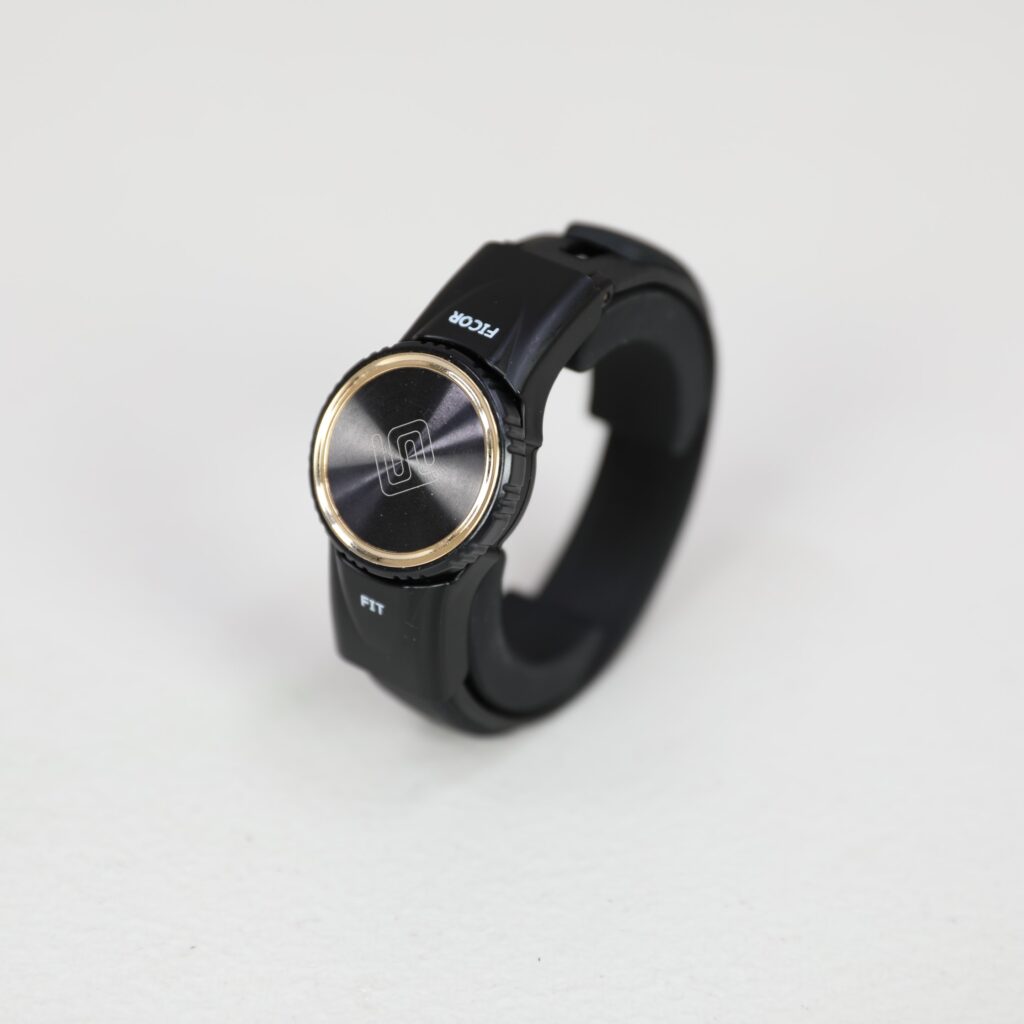
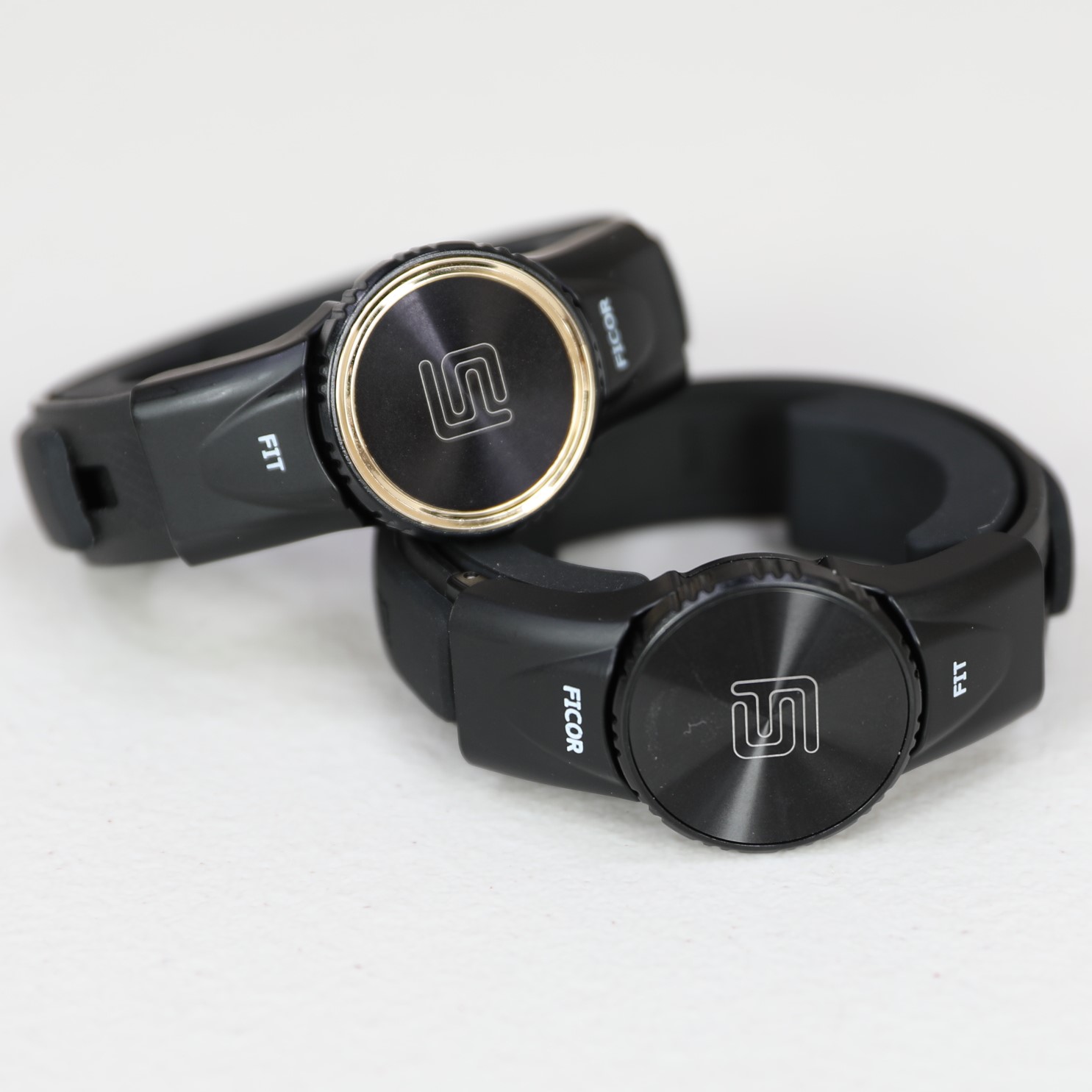
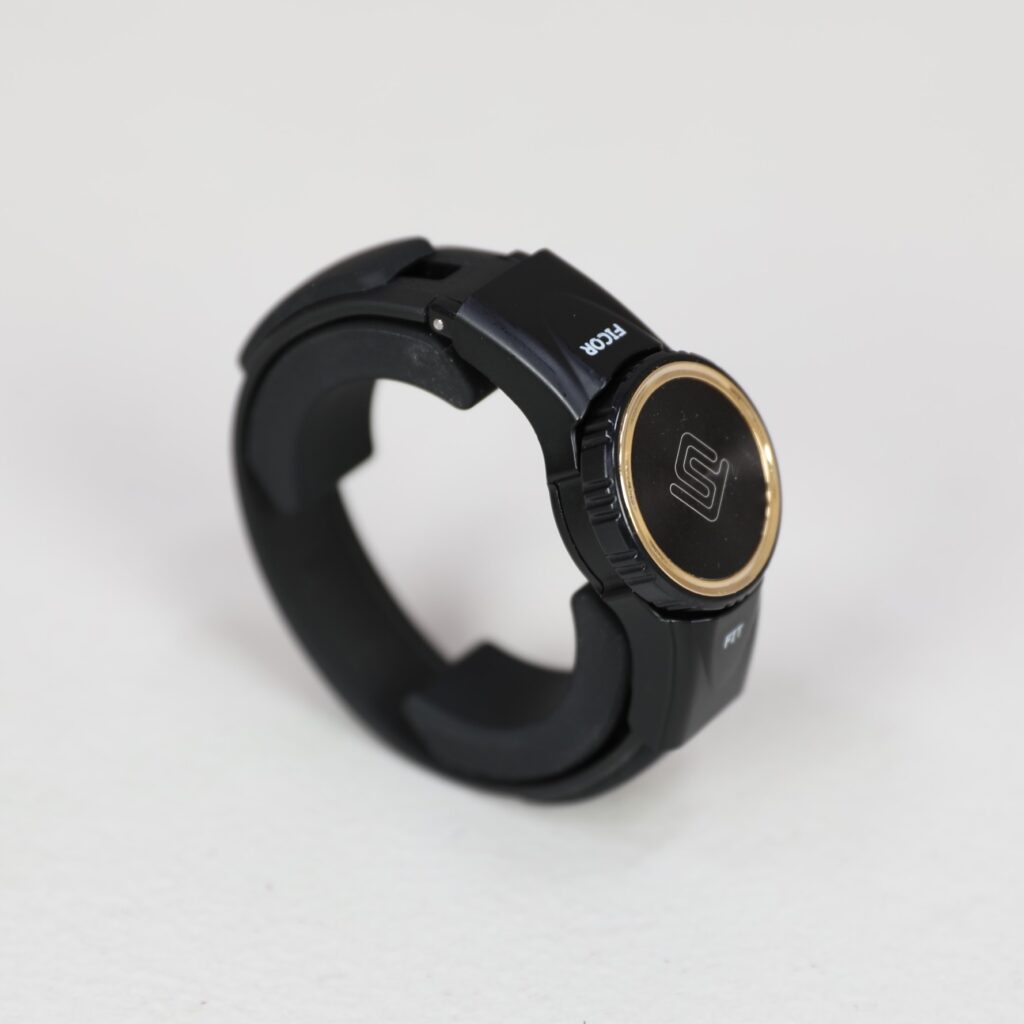
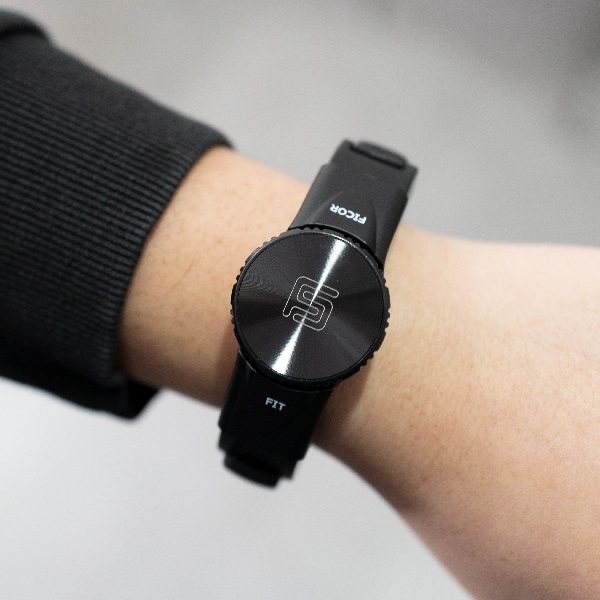
Wrist Tendon Pain Wristband
Ulnar Tendonitis Pain Relief
What is wrist tendonitis?
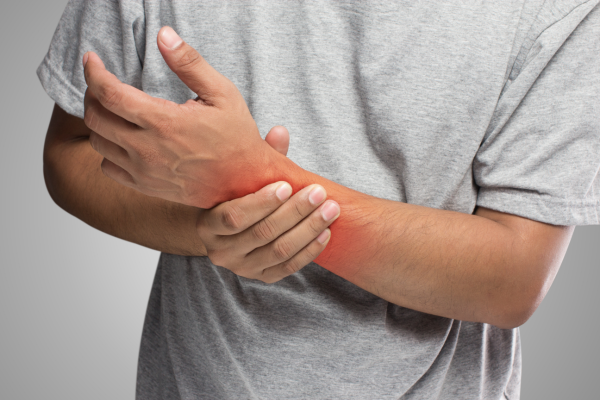
Wrist tendonitis, also known as tenosynovitis or tendinitis, is a condition characterized by inflammation or irritation of the tendons that surround the wrist joint, which has been increasing due to the use of technology. Tendons are strong, fibrous tissues that connect muscles to bones, and they play an important role in the movement of joints. In the case of wrist tendonitis, the tendons in the wrist become inflamed, leading to pain, swelling, and discomfort.
What are the causes of wrist tendonitis pain?
Common causes and risk factors of wrist tendonitis include:
Overuse or Repetitive Strain: Activities that involve repetitive wrist movements or strain, such as typing, playing musical instruments, or using tools, can lead to wrist tendonitis.
Injury or Trauma: A wrist tendonitis injury or trauma to the wrist, such as a fall or impact, can damage the wrist tendons and trigger inflammation.
Poor Ergonomics: Improper ergonomics, such as an inadequately set up workspace, can contribute to wrist strain and inflammation.
Aging: As individuals age, tendons may become less flexible and more prone to inflammation and injury.
Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, can increase the risk of developing wrist tendonitis.
Symptoms of Wrist Tendonitis
 Common symptoms of wrist tendonitis include:
Common symptoms of wrist tendonitis include:
Pain: Pain is the most prominent symptom of wrist tendonitis. It is typically localized to the wrist and can range from mild to severe. The pain may be sharp, dull, or aching in nature.
Swelling: Inflammation of the tendons and their sheaths can lead to swelling around the affected area. This swelling may be visible as an increased fullness or puffiness in the wrist region.
Tenderness: The wrist may be tender to the touch, particularly over the affected tendon. Pressing on the tender area may exacerbate the pain.
Stiffness: Individuals with wrist tendonitis may experience stiffness in the wrist joint. This can make it difficult to move the wrist freely and may lead to decreased range of motion.
Weakness: Some people with wrist tendonitis may notice weakness in the affected hand and wrist. This can affect grip strength and fine motor skills.
Crepitus: In some cases, there may be a cracking or popping sensation (crepitus) when moving the wrist. This is often due to friction between inflamed tendons and their surrounding structures.
Pain with Activity: Pain and discomfort associated with wrist tendonitis often worsen during activities that involve repetitive wrist motions, gripping, or lifting heavy objects. Activities like typing, playing musical instruments, or using tools can exacerbate the symptoms.
Pain at Rest: In more severe cases, wrist tendonitis may cause pain even at rest, particularly during the night or upon waking in the morning.
Radiating Pain: Pain from the wrist may radiate up the forearm or down into the hand and fingers. This can sometimes be confused with other conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome.
What’s the recovery time for ulnar tendonitis?
The recovery time for ulnar tendonitis varies based on its severity and treatment. Ulnar tendonitis is characterized by inflammation or irritation of the tendons on the ulnar (inner) side of the wrist. Mild cases may resolve in a few weeks to a couple of months with rest, while more severe cases or surgery can extend the recovery to several weeks or months. Individual responses to treatment differ; follow a healthcare provider’s guidance for a specific recovery timeline. Treatments may include rest, icing, anti-inflammatory medications, immobilization with a splint or brace, and physical therapy. If there is significant tendon damage, treatment may involve corticosteroid injections, regenerative therapies, or, in rare cases, surgical intervention.

Are you suffering from Wrist Tendonitis?
Experience the pain-relieving design
of the Ficor Goldilocks wristband
What are common wrist tendonitis treatment options at home?
Wrist tendonitis treatments at home typically involve conservative measures, including:
Rest: Resting the affected wrist by avoiding or modifying activities that exacerbate symptoms.
Ice: Applying ice to the affected area to reduce inflammation and pain. Use a cloth or towel to protect the skin and apply ice for 15-20 minutes at a time.
Compression: Wearing a wrist brace or bandage to provide support and reduce strain on the tendons.
Elevation: Keeping the wrist elevated when resting to minimize swelling.
Anti-Inflammatory Medications: Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may help reduce pain and inflammation.
Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can provide exercises and stretches to improve wrist strength and flexibility.
Corticosteroid Injections: In some cases, a healthcare provider may recommend corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation and pain.
Activity Modification: Making changes to daily activities and ergonomics to prevent further strain on the wrist.
In severe cases or when conservative treatments do not provide relief, surgery may be considered to repair or release the affected tendons. Consult a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan if you suspect you have wrist tendonitis to prevent further complications and promote healing.
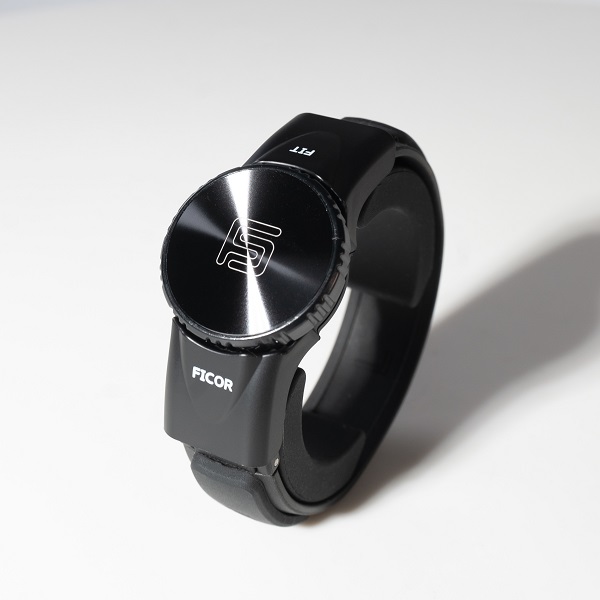
How can the Ficor Fit band help relieve pain from tendonitis in the wrist?
The Ficor Fit wristband delivers unparalleled ergonomic support by stabilizing the wrist and promoting proper alignment that minimizes tendon stress. It secures the unstable pillar bones while stabilizing the radioulnar joint, reducing pain in the wrist and the forearm, and allowing for comfortable movement of your wrist. The lower part of the Ficor Fit wristband lessens the pressure on the nervous system. The Ficor Fit band is expertly constructed of medical-grade silicone and Thermo Plastic Elastomer (TPE) material, reducing moisture absorption, minimizing bacteria growth, and ensuring a comfortable, secure fit. This wristband strikes the perfect balance between compression and flexibility.
What makes the Ficor Fit band better for wrist tendonitis than a traditional wrist brace?
The Ficor Fit band is a more powerful tool in the fight against tendonitis than traditional wrist braces. It consistently delivers support and comfort to help you regain control of your daily activities. If you are typing at your computer, scrolling through your phone, or playing a repetitive sport, the cutting-edge wrist support of the Ficor Fit wristband delivers optimal pain-free relief and protection against tendonitis, so you can fully participate in all areas of your life.
You can also wear our Ficor Fit or our Ficor Goldilocks wristbands to help with Carpal Tunnel, Golfer’s Elbow, Tennis Elbow, Sprained Wrist, and De Quervain’s Syndrome.
Wrist Pain Symptoms
Symptoms of CTS include pain and tingling in the wrist & fingers, numbness/weakness in the hand.
Golfer’s elbow occurs when the tendons and muscles in the forearm are overused.
The symptoms of Tennis Eblow can include pain, swelling, and stiffness in the elbow.
Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI) is caused by repetitive motions such as typing, sewing, or using a mouse.
Triangular Fibrocartilage injuries are caused by overuse or misuse of a muscle or joint.
Wrist tendonitis is inflammation of the wrist tendons and can affect all ages.
Wrist sprains are characterized by twisting or rotating the wrist suddenly.
De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis causes pain and tingling in the wrist or hand.







© Ficor Health, Inc. | All Rights Reserverd